Functions
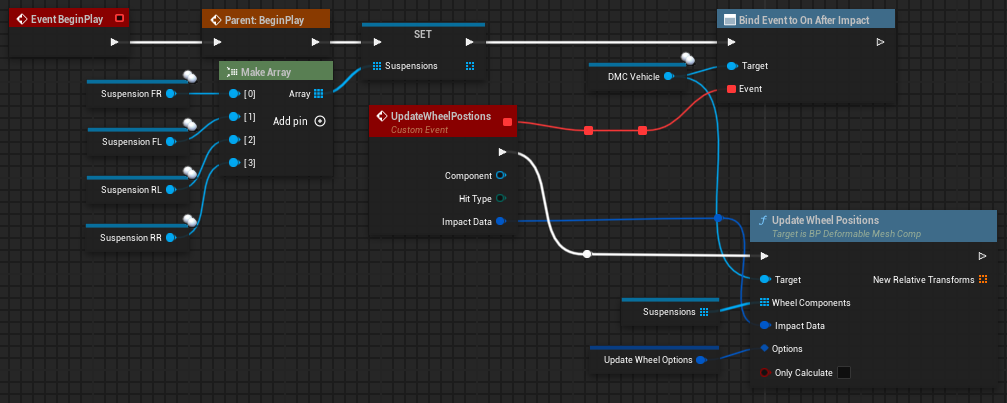
Add Hit at Location
Perform a manual hit and (optionally) apply an impulse to the actor.
Hit Location & Hit Location Type: Where should the hit go? (relative or world location)
Impact Strength: Strength of the impact (). This affects the hit radius and the strength should be between 0 and MaxHitAcceleration!
Add Impulse: Whether to apply an impulse or not (instantaneous force, see unreal's original AddImpulseAtLocation for reference)
Impulse: Magnitude and direction of impulse to apply. (Unit: )
Impulse in World Space: Impulse in relative or world space?
✅ Network replicated
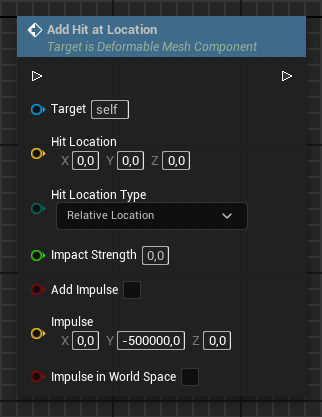
Reset Deformation
Reset the deformation and optionally refresh the mesh itself.
Should Update Mesh: Without this the reset deformation will not be visible (until the next hit happened).
✅ Network replicated
Update mesh
This will refresh the visible mesh (e.g. after Reset Deformation). Normally you don't have to call this manually.
❌ Only local
Change Deformable Mesh
This function is included in Version 2.2.

Using this function you can change the deformable mesh at runtime while you play. It resets the deformation and calling this is probably expansive (performance-wise), depending on your mesh. Don't call it too frequently.
This can be called in begin play, but try not to call this when a hit is currently being processed. We have already taken some internal precautions to prevent it from crashing when the mesh is changed while a hit is being processed, but this should be prevented in general if possible.
Note: This only changes the deformable mesh but it does not change the static mesh of the parent component or the Material Overrides. This must be done manually! See example below.
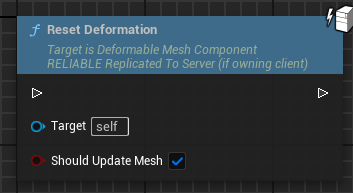
Example usage (BP_DeformationExampleStaticMesh)
The following functions switches between two deformable meshes.
Whenever a deformable mesh is loaded (this is also the case after calling ChangeDeformableMesh) we change the parent components static mesh to the static mesh of the loaded deformable mesh so it uses a suitable collision (optionally if both deformable meshes are very similar). Additionally we may have to assign different Material Overrides.
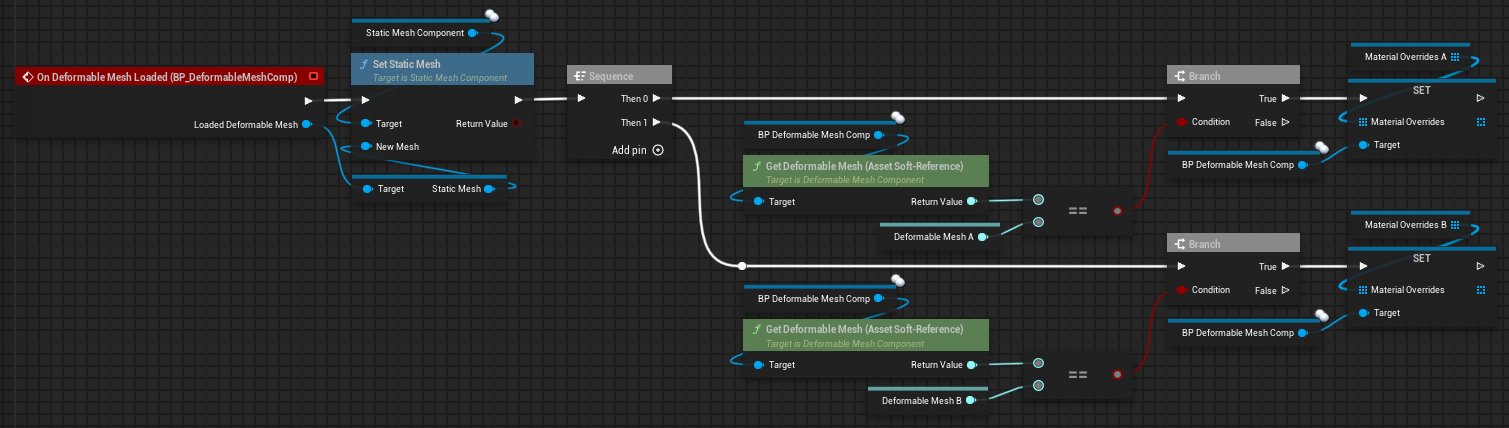
✅ Network replicated (make sure to change the static mesh and material overrides manually if necessary)
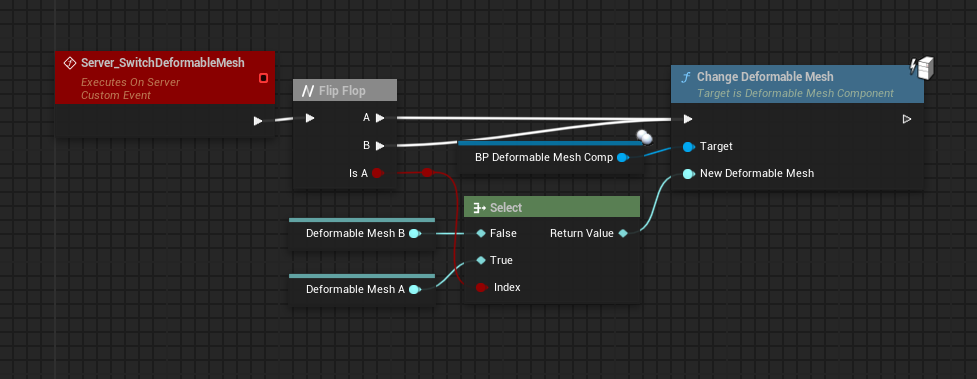
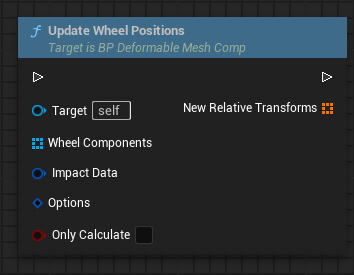
Update Wheel Positions
This function is included in Version 2.2.
This is a R-Tune exclusive function at the moment. That means this function officially is only compatible with R-Tune. There will be an example using our police car.
This function will move and tilt your wheels on impact depending on where the hit happened. This function should be called after impact. See Example Usage below.
- Wheel Component: Your suspension components (not the actual wheels).
- Impact Data: This comes from the AfterImpact and should be passed through.
- Options:
- Max Displacement: Maximum displacement relative to default position.
- Displacement Multiplier: Influences how far the component is moved / displaced.
- Max Tilt: Maximum tilt of the component (in degrees).
- Tilt Multiplier: Influences how steeply the component tilts.
- Only Calculate: If this is true, the components will not be changed. You can use the output transforms to manually change the components.
✅ Network replicated (call on server and make sure the suspension components are replicated)
Example usage
Suspension contains all suspension components that will be moved. You should not change the order the elements or dynamically add/remove elements.
Update Wheel Options is a variable inside that car actor, that contains appropriate values for that actor.